Drug Abuse and Addiction in Illinois
Drug addiction presents a complex and multifaceted challenge in Illinois, impacting individuals, families, and communities across the state. Its effects span health, social, and economic domains, leading to profound consequences that necessitate comprehensive responses.
Jump to Section
Illinois Drug Use Fast Facts
According to the Illinois Department of Public Health and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), issues regarding drug addiction have increased over the span of several years.
- Opioid Overdose Deaths: Illinois has seen a significant rise in deaths attributed to opioids, including prescription opioids, heroin, and particularly synthetic opioids like fentanyl.
- Prescription Drug Misuse: A substantial number of individuals misuse prescription drugs, often obtaining them from friends or relatives, highlighting the need for secure medication storage and cautious prescribing.
- Heroin and Fentanyl Crisis: The state faces a severe challenge with heroin, especially fentanyl, which is notably more potent and has been linked to a considerable increase in overdose fatalities.
- Youth Drug Use: Marijuana is the most commonly used illicit substance among Illinois youth, with prescription drugs also being misused for non-medical reasons.
Treatment and Recovery Services Demand: The demand for inpatient drug and alcohol rehabs in Illinois indicates a significant need for accessible care options, though many still do not receive the help they need.
How Does Drug Addiction Impact Illinois?
Get the help you need at Northern Illinois Recovery!
855.458.1739
Northern Illinois Recovery Addiction Treatment Center


Health Impacts and Overdoses
Drug overdose is a leading cause of preventable death in Illinois, with opioids, particularly fentanyl, driving a significant increase in fatalities. The rising trend in overdose deaths not only reflects the severity of drug addiction but also underscores the urgent need for effective drug intervention and treatment strategies.
Spread of Infectious Diseases
Intravenous drug use is a key factor in the spread of infectious diseases such as HIV/AIDS and hepatitis C. Sharing needles, and other drug paraphernalia increases the risk of transmission, posing public health challenges that require targeted prevention and education efforts.


Social Impacts of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction can lead to family breakdowns, with children often the most affected. It can result in parental neglect, abuse, and a higher likelihood of children entering the foster care system. Communities also suffer from increased crime rates, including drug trafficking and related violence, contributing to a cycle of instability and insecurity.
There’s a strong correlation between drug addiction and co-occurring mental health disorders. Individuals with substance use disorders are more likely to experience conditions such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis. This bidirectional relationship complicates treatment and recovery, emphasizing the need for integrated care approaches.


Economic Impacts of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction affects the state’s workforce through increased absenteeism, decreased productivity, and higher rates of workplace accidents. Businesses incur significant costs due to these issues, alongside increased healthcare expenses and insurance premiums.
The economic burden extends to public resources, with increased demand for healthcare services, law enforcement, and criminal justice interventions. Funding for addiction treatment and prevention programs, while essential, also places a strain on state budgets.
Addressing the Challenge of Drug Addiction
The state of Illinois has implemented various strategies to combat drug addiction, focusing on enhancing access to treatment, expanding harm reduction services such as needle exchange programs, and increasing the availability of Naloxone to reverse opioid overdoses.
Collaborative efforts involving government agencies, healthcare providers, community organizations, and law enforcement aim to tackle the root causes of addiction, provide support for those affected, and reduce the overall impact on the state.
At Northern Illinois Recovery Center, we offer a range of services to help individuals recover from drug and alcohol addiction. We offer drug and alcohol detox, inpatient treatment, outpatient treatment programs, and aftercare services for residents of Illinois and people from all across the country. Some of the types of addiction we treat include:


Alcohol addiction, also known as alcohol use disorder, is a chronic condition characterized by an inability to control or stop drinking despite adverse consequences. It often leads to significant health, social, and psychological issues. Treatment for alcohol addiction typically involves a combination of therapies, including detoxification, counseling, medication, and support groups, all aimed at helping individuals manage withdrawal symptoms, address underlying psychological issues, and develop coping mechanisms for long-term sobriety.
Alcohol-Related Topics
- Alcoholism Quiz
An alcoholism quiz can help determine if you have a drinking problem by asking specific questions about your drinking habits, the impact of alcohol on your daily life, and any physical or psychological symptoms you may be experiencing. - Alcohol Withdrawal Medication
Alcohol withdrawal medication includes drugs prescribed to help manage the symptoms and reduce the risks associated with alcohol withdrawal. - Quitting Alcohol Cold Turkey
Quitting alcohol “cold turkey” means abruptly stopping all alcohol consumption without gradually reducing intake or using any medications to ease withdrawal symptoms.
Drug addiction, or substance use disorder, is a chronic disease characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use despite harmful consequences. It affects brain function and behavior, leading to an inability to control drug intake.
Illicit Drugs related topics
- Cocaine Treatment
Treatment often focuses on behavioral therapies to help individuals overcome cocaine addiction. - Heroin Treatment
Heroin treatment process typically starts with medically supervised detoxification to manage withdrawal symptoms safely. Therapies, support groups, and a treatment plan are essential. - Inhalant Treatment
Treatment for inhalant addiction involves a multi-faceted approach tailored to address the unique challenges posed by these substances. The process generally begins with a thorough medical and psychological assessment to determine the extent of the addiction- Whippits
“Whippits” is a slang term for small canisters of nitrous oxide, often used as a recreational inhalant drug. Misuse of whippits can be dangerous, leading to short-term effects like impaired motor function and long-term health risks, including nerve damage, oxygen deprivation, and even death due to asphyxiation.
- Whippits
- Ketamine Treatment
Ketamine addiction is a condition characterized by the compulsive use and abuse of ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic that can produce hallucinogenic effects. Treatment for ketamine addiction involves a comprehensive, multi-faceted approach designed to address the physical, psychological, and social aspects of the addiction. - Marijuana Treatment
Though often perceived as less addictive, treatment is available for those struggling with marijuana use disorder. - Methamphetamine Treatment
Providing comprehensive treatment that includes both medical and psychological support. - Party Drugs
Treatment for addiction to party drugs, which include substances like MDMA (Ecstasy), LSD, ketamine, and GHB, involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction. - Opiates
Opiate addiction, also known as opioid use disorder, is a chronic condition characterized by the compulsive use of opiate drugs despite harmful consequences. Opiates include natural substances derived from the opium poppy, such as morphine and codeine, as well as synthetic opioids like heroin, fentanyl, oxycodone, and hydrocodone. - Fentanyl Treatment
Fentanyl is a powerful synthetic opioid that is significantly more potent than morphine or heroin, making addiction and overdose risks particularly high. - Opioid Treatment
Including prescription painkillers as well as illicit drugs like heroin, with treatments often involving medication-assisted therapy. - OxyContin Treatment
OxyContin is a powerful opioid prescribed to treat moderate to severe pain, but its high potential for addiction has made it a significant contributor to the opioid crisis. - Tramadol Treatment
Although tramadol is considered to have a lower potential for abuse compared to other opioids, it still poses significant risks for dependence and addiction.
This type of addiction can involve various classes of medications, including opioids, benzodiazepines, stimulants, and others. Despite being legally prescribed, these drugs carry significant risks for dependence and addiction when misused.
Prescription Drugs related topics:
- Barbiturate Treatment
Barbiturates are primarily used for their sedative, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant properties, but their high potential for addiction and risk of overdose have led to a decline in their medical use over the years. - Benzodiazepine Treatment
Benzodiazepines are commonly prescribed for anxiety, insomnia, muscle relaxation, and seizure management. Despite their therapeutic benefits, they carry a high risk of dependence and addiction. - Xanax Treatment
Xanax addiction is a form of benzodiazepine addiction specifically related to the misuse of Xanax, which is the brand name for alprazolam. At NIRC, we offer programs specifically for individuals dealing with Xanax addiction.
Stimulant drug addiction is a form of substance use disorder characterized by the compulsive use and abuse of stimulant drugs, which are substances that increase activity in the brain and nervous system. Stimulants can be either prescription medications or illicit drugs, and they are known for their stimulating effects, such as increased alertness, energy, and euphoria.
Stimulants related topics:
- Anabolic Steroids
These substances are often used to enhance muscle mass, strength, and athletic performance, but they carry significant risks for dependence and various health issues.
- Alcohol
-
Alcohol addiction, also known as alcohol use disorder, is a chronic condition characterized by an inability to control or stop drinking despite adverse consequences. It often leads to significant health, social, and psychological issues. Treatment for alcohol addiction typically involves a combination of therapies, including detoxification, counseling, medication, and support groups, all aimed at helping individuals manage withdrawal symptoms, address underlying psychological issues, and develop coping mechanisms for long-term sobriety.
Alcohol-Related Topics
- Alcoholism Quiz
An alcoholism quiz can help determine if you have a drinking problem by asking specific questions about your drinking habits, the impact of alcohol on your daily life, and any physical or psychological symptoms you may be experiencing. - Alcohol Withdrawal Medication
Alcohol withdrawal medication includes drugs prescribed to help manage the symptoms and reduce the risks associated with alcohol withdrawal. - Quitting Alcohol Cold Turkey
Quitting alcohol “cold turkey” means abruptly stopping all alcohol consumption without gradually reducing intake or using any medications to ease withdrawal symptoms.
- Alcoholism Quiz
- Illicit Drugs
-
Drug addiction, or substance use disorder, is a chronic disease characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use despite harmful consequences. It affects brain function and behavior, leading to an inability to control drug intake.
Illicit Drugs related topics
- Cocaine Treatment
Treatment often focuses on behavioral therapies to help individuals overcome cocaine addiction. - Heroin Treatment
Heroin treatment process typically starts with medically supervised detoxification to manage withdrawal symptoms safely. Therapies, support groups, and a treatment plan are essential. - Inhalant Treatment
Treatment for inhalant addiction involves a multi-faceted approach tailored to address the unique challenges posed by these substances. The process generally begins with a thorough medical and psychological assessment to determine the extent of the addiction- Whippits
“Whippits” is a slang term for small canisters of nitrous oxide, often used as a recreational inhalant drug. Misuse of whippits can be dangerous, leading to short-term effects like impaired motor function and long-term health risks, including nerve damage, oxygen deprivation, and even death due to asphyxiation.
- Whippits
- Ketamine Treatment
Ketamine addiction is a condition characterized by the compulsive use and abuse of ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic that can produce hallucinogenic effects. Treatment for ketamine addiction involves a comprehensive, multi-faceted approach designed to address the physical, psychological, and social aspects of the addiction. - Marijuana Treatment
Though often perceived as less addictive, treatment is available for those struggling with marijuana use disorder. - Methamphetamine Treatment
Providing comprehensive treatment that includes both medical and psychological support. - Party Drugs
Treatment for addiction to party drugs, which include substances like MDMA (Ecstasy), LSD, ketamine, and GHB, involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction. - Opiates
Opiate addiction, also known as opioid use disorder, is a chronic condition characterized by the compulsive use of opiate drugs despite harmful consequences. Opiates include natural substances derived from the opium poppy, such as morphine and codeine, as well as synthetic opioids like heroin, fentanyl, oxycodone, and hydrocodone. - Fentanyl Treatment
Fentanyl is a powerful synthetic opioid that is significantly more potent than morphine or heroin, making addiction and overdose risks particularly high. - Opioid Treatment
Including prescription painkillers as well as illicit drugs like heroin, with treatments often involving medication-assisted therapy. - OxyContin Treatment
OxyContin is a powerful opioid prescribed to treat moderate to severe pain, but its high potential for addiction has made it a significant contributor to the opioid crisis. - Tramadol Treatment
Although tramadol is considered to have a lower potential for abuse compared to other opioids, it still poses significant risks for dependence and addiction.
- Cocaine Treatment
- Prescription Drugs
-
This type of addiction can involve various classes of medications, including opioids, benzodiazepines, stimulants, and others. Despite being legally prescribed, these drugs carry significant risks for dependence and addiction when misused.
Prescription Drugs related topics:
- Barbiturate Treatment
Barbiturates are primarily used for their sedative, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant properties, but their high potential for addiction and risk of overdose have led to a decline in their medical use over the years. - Benzodiazepine Treatment
Benzodiazepines are commonly prescribed for anxiety, insomnia, muscle relaxation, and seizure management. Despite their therapeutic benefits, they carry a high risk of dependence and addiction. - Xanax Treatment
Xanax addiction is a form of benzodiazepine addiction specifically related to the misuse of Xanax, which is the brand name for alprazolam. At NIRC, we offer programs specifically for individuals dealing with Xanax addiction.
- Barbiturate Treatment
- Stimulants
-
Stimulant drug addiction is a form of substance use disorder characterized by the compulsive use and abuse of stimulant drugs, which are substances that increase activity in the brain and nervous system. Stimulants can be either prescription medications or illicit drugs, and they are known for their stimulating effects, such as increased alertness, energy, and euphoria.
Stimulants related topics:
- Anabolic Steroids
These substances are often used to enhance muscle mass, strength, and athletic performance, but they carry significant risks for dependence and various health issues.
- Anabolic Steroids
Signs and Symptoms of Drug Addiction and Misuse
Drug addiction, also known as substance use disorder, encompasses a range of physical, psychological, and behavioral signs and symptoms that can vary depending on the substance used, the duration of addiction, and individual differences. Recognizing these signs can be pivotal in seeking help early. Here are some of the common symptoms associated with drug addiction:
- Changes in Appearance: Sudden weight loss or gain, poor hygiene, and changes in skin condition.
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or excessive sleeping.
- Physical Dependence: Experiencing withdrawal symptoms such as shaking, sweating, nausea, or headaches when not using the drug.
- Tolerance: Needing increasingly larger amounts of the substance to experience the same effects
- Mood Swings: Rapid and unexplained changes in mood.
- Increased Irritability or Aggression: Especially if the drug is not available.
- Anxiety and Paranoia: Feeling constantly worried, anxious, or overly suspicious.
- Depression: Persistent sadness, low energy, and loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities.
- Neglecting Responsibilities: Failing to meet work, school, or family obligations.
- Social Withdrawal: Isolating oneself from friends and family, or abandoning hobbies.
- Risky Behaviors: Engaging in dangerous activities, especially when under the influence, or to obtain the substance.
- Secrecy and Lying: Being secretive about activities or lying about the amount and frequency of drug use.
- Financial Issues: Spending significant amounts of money on drugs, borrowing money frequently, or stealing to fund drug use.
- Impaired Judgment: Difficulty making decisions or remembering important information.
- Obsession with Substance: Spending a lot of time thinking about, obtaining, using, and recovering from the effects of the substance.
- Denial: Refusing to acknowledge the negative consequences of their drug use.
Recognizing these signs in oneself or others can be the first step toward seeking treatment and recovery. Drug addiction is a complex disease, but with the right support and intervention, recovery is possible.




The Unfortunate Effects of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction can lead to a plethora of short and long-term effects that impact nearly every aspect of an individual’s life. These effects vary based on the type of drug, the amount and frequency of use, and the person’s overall health and background. Understanding these effects is crucial for recognizing the seriousness of substance use disorders and the importance of seeking help.
In the short term, drug addiction can cause immediate changes in physical health, cognition, and behavior, including:
- Physical Health: Increased heart rate, blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, fluctuation in appetite, and in the case of stimulants, heightened alertness or, conversely, sedation and drowsiness with depressants.
- Cognitive Impairments: Reduced ability to make decisions, impaired judgment, memory lapses, and difficulty concentrating.
- Behavioral Changes: Risk-taking behaviors, such as driving under the influence, using dirty needles, or engaging in unprotected sex, leading to injury or transmission of infectious diseases.
- Psychological Effects: Anxiety, paranoia, mood swings, aggression, and initial euphoria followed by periods of depression.
The long-term effects of drug addiction can be more severe, affecting physical and mental health, social relationships, and overall quality of life:
- Chronic Health Issues: Liver damage, heart disease, lung disease, kidney failure, and infectious diseases like HIV/AIDS and hepatitis C from needle sharing.
- Mental Health Disorders: Prolonged drug use can exacerbate or contribute to the development of mental health disorders like depression, anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
- Cognitive Decline: Long-term substance abuse can result in cognitive impairments, affecting learning, memory, and problem-solving abilities.
- Social and Economic Impact: Strained or broken relationships, loss of employment, financial instability, homelessness, and involvement in criminal activities.
- Addiction and Dependence: Physical dependence can develop, leading to withdrawal symptoms when not using the drug, and psychological addiction can make quitting extremely difficult without professional help.
- Overdose Risk: Increased tolerance and physical dependence may lead to consuming higher doses to achieve the same effects, significantly raising the risk of overdose, which can be fatal.
Drug Addiction Frequently Asked Questions
There’s no single cause; it’s typically a combination of factors including genetics, environment, and personal history of trauma or other mental health issues.
While the terms are often used interchangeably, addiction is characterized by a physical or psychological dependency on substances, leading to compulsive drug seeking and use despite harmful consequences. Abuse can exist without addiction, but frequent abuse can lead to addiction.
Yes, there are various effective treatments available, including medication, counseling, behavioral therapies, and support groups. Treatment plans should be individualized, addressing not only the substance use disorder but also any underlying mental health conditions.
Approach them with empathy and concern, avoiding judgment or confrontation. Encourage them to speak about their issues and offer to help them find professional support or treatment options.
Yes, treatment strategies may vary depending on the substance involved and the individual’s needs. For instance, opioid abuse might be treated with specific medications like methadone or buprenorphine, whereas other forms of drug abuse might focus more on psychotherapy and support groups.
Drug abuse can exacerbate existing mental health disorders or lead to the development of new ones, such as depression, anxiety, or psychosis. The relationship between drug abuse and mental health is complex and bidirectional.
Prevention is crucial and involves educating individuals, especially young people, about the risks of drug use, promoting healthy lifestyles, and developing skills to resist peer pressure. Community-based efforts and policies that limit access to drugs are also important.
Northern Illinois Recovery Center Can Help


If you or a loved one are dealing with drug addiction, NIRC can be a resource for you. We have some of the top drug addiction specialists and therapists in the country. Give us a call if you have any questions or would like to discuss or programs.
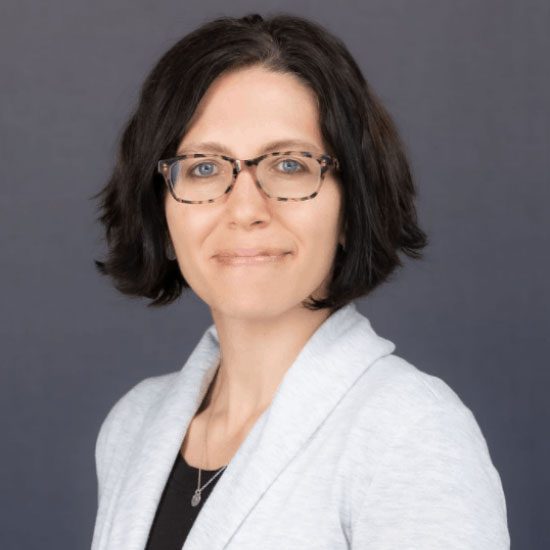


Licensed Physician and Surgeon
Dr. Beth Dunlap, a board-certified addiction medicine and family medicine physician, and is the medical director at Northern Illinois Recovery Center. She is responsible for overseeing all the integrated medical services at both campuses. Beth completed medical school, residency, and fellowship at Northwestern University, where she continues to serve on the faculty as a member of the Department of Family and Community Medicine. She has extensive experience in addiction medicine at all levels of care, and her clinical interests include integrated primary care and addiction medicine, harm reduction, and medication-assisted treatment.