May is Stroke Awareness Month—a moment to educate, engage, and empower people about the effects that drug abuse can have on the brain and body. This month calls on all of us to recognize the warning signs of a stroke, understand the risks, and embrace the hope that recovery is possible with timely intervention. While common risk factors of a stroke, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking, are widely discussed, another significant contributor often flies under the radar: drug use.
Many people, especially younger individuals, may not realize that substance abuse can dramatically increase their risk of experiencing a stroke, a potentially devastating medical emergency. Understanding this connection is vital for prevention and highlights the importance of addressing addiction for overall health.
This blog post delves into how drug use can trigger strokes, the types of drugs most commonly abused, and the steps one can take toward recovery and risk reduction. If you’re unsure about your own habits, take our Do I Have an Addiction Quiz to better understand your risk.
What Is A Stroke?
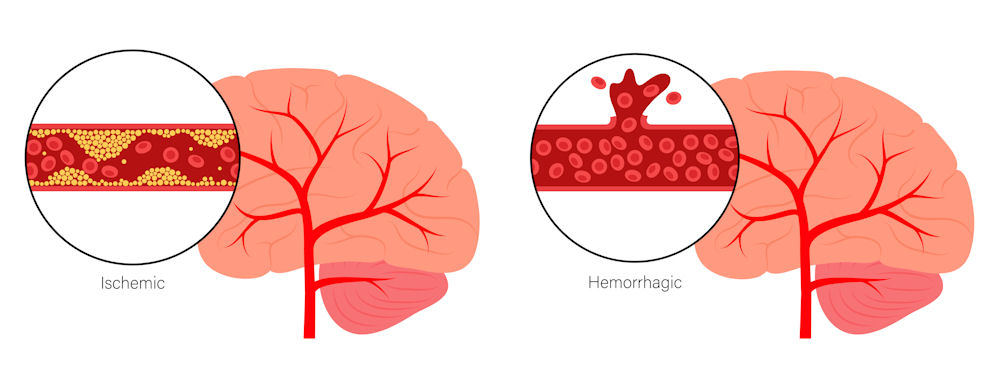 The blood vessels’ job in the body is to carry oxygen and nutrients to the brain. When blood flow to a part of the brain is suddenly interrupted and the body isn’t receiving the resources it needs to function properly, the blood vessels die. As a result, a stroke, known as a brain attack, occurs due to a blockage/clot (ischemic stroke) or a ruptured blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke).
The blood vessels’ job in the body is to carry oxygen and nutrients to the brain. When blood flow to a part of the brain is suddenly interrupted and the body isn’t receiving the resources it needs to function properly, the blood vessels die. As a result, a stroke, known as a brain attack, occurs due to a blockage/clot (ischemic stroke) or a ruptured blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke).
Strokes can cause a wide range of symptoms depending on the area of the brain affected, such as sudden numbness, confusion, trouble speaking, or loss of coordination. Some strokes are temporary, like a transient ischemic attack (TIA), often called a “mini-stroke,” which serves as a warning sign for a future major stroke. A stroke can be fatal if not treated immediately, resulting in serious brain damage or death. Early recognition and immediate medical attention are crucial for improving recovery and reducing long-term effects.
Types of Strokes
Drug abuse can lead to different forms of stroke, depending on how the substances affect the brain and blood vessels.
This happens when a drug triggers a blood clot or narrows blood vessels, blocking blood flow to the brain. Stimulants like cocaine, methamphetamine, or synthetic drugs can rapidly raise blood pressure and tighten arteries, leading to a clot.
Some drugs cause a sudden spike in blood pressure or weaken vessel walls, leading to a burst blood vessel in the brain. This is common with cocaine, amphetamines, or high alcohol intake, which can all cause vessel rupture and bleeding.
Drug use can also cause a temporary blockage of blood flow, leading to a mini-stroke. Though symptoms go away quickly, it’s a serious warning sign of a full stroke risk, especially with repeated substance abuse.
What Causes Strokes?
Strokes are mainly attributed to two primary factors: an obstruction of blood flow to the brain or the occurrence of bleeding within the brain. An ischemic stroke results from a blocked artery in the brain due to blood clots or the accumulation of plaque, while a hemorrhagic stroke is caused by the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain.
Some individuals may experience a temporary interruption of blood flow to the brain, referred to as a transient ischemic attack (TIA). Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a stroke is crucial to saving lives. Several factors can contribute to the onset of a stroke, including:

- Family History (Genetics)
- Age
- High blood pressure (Hypertension)
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
Blood clots may develop due to coronary heart disease, atrial fibrillation, heart valve disease, and carotid artery disease. A familial history of strokes can elevate your risk (If close family members have had one, due to shared health patterns or genetics). The likelihood of having a stroke also increases as we age.
Hypertension significantly increases the risk for both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
Smoking is an unhealthy habit that significantly increases stroke risk by damaging blood vessel linings, speeding up artery-clogging plaque buildup, raising blood pressure, and more prone of blood clots.
Elevated blood sugar levels can harm blood vessels and heighten the likelihood of stroke. High blood sugar damages blood vessels over time, making them more likely to clog or burst, both of which can lead to a stroke.
Hypertension significantly increases the risk for both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
Being overweight, especially around the belly, raises the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease—all of which can lead to stroke. Extra body fat also affects how well your body handles blood flow and inflammation.
Heavy drinking raises blood pressure and weakens the heart, making a stroke more likely, especially with frequent or binge drinking. Over time, excessive drinking often leads to an alcohol use disorder (AUD).
Lack of exercise slows blood flow, leads to weight gain, and raises stroke risk by causing high blood pressure and poor circulation.
While these causes of a stroke are well-known and commonly discussed, another risk factor that is often overlooked and increasingly becoming a major concern is drug use.
Can Drugs Cause a Stroke?
Some drugs, especially illicit or abused substances, can significantly raise the risk of stroke. These drugs can negatively impact both the heart and brain by triggering high blood pressure, abnormal heart rhythms, and the formation of blood clots—factors that can all contribute to a stroke. Here are some common drugs that have been linked to an increased risk of stroke:
One of the most notorious drugs for causing strokes, cocaine abuse can cause the blood vessels in the brain to constrict, leading to a reduction in blood flow. Cocaine can also increase blood pressure and heart rate, which contributes to the risk of both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
Meth abuse can cause the blood vessels in the brain to tighten, raising the risk of ischemic strokes. Methamphetamine use can also cause arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), which increases the risk of blood clots and stroke.
While heroin does not directly cause strokes in the same way as cocaine or meth, long-term heroin abuse can lead to complications such as high blood pressure, blood clots, and cardiovascular issues—all of which can increase stroke risk.
While marijuana is often seen as a safer drug, its use has been linked to a slight increase in stroke risk. Research suggests that marijuana use may increase heart rate and blood pressure, potentially triggering stroke events, particularly in those who are already at risk.
Known as “K2” or “Spice,” these synthetic drugs can cause severe health complications, including strokes. They can induce dangerously high blood pressure and heart rate, increasing the chances of both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
Misusing prescription drugs, such as opioids and stimulants, can also elevate stroke risk. For example, excessive use of stimulants can cause high blood pressure and increase the likelihood of a stroke.
Drug-Induced Stroke Symptoms
Stroke symptoms can differ based on the stroke type and the specific brain region involved. In cases related to drug use, typical warning signs may include:
- Numbness or weakness appearing without warning, predominantly on one side of the body (face, arm, or leg)
- Confusion, difficulty speaking, or trouble understanding speech
- Sudden changes in your vision, including blurriness, loss of sight in one or both eyes, or seeing double
- Problems with coordination, including difficulty walking, experiencing dizziness, or loss of balance
- Severe headache with no known cause
Don’t wait if stroke symptoms occur. Call 911 and reach out for medical attention immediately! Early treatment can save brain function and improve the chance of recovery after a stroke. Waiting to get help will result in dire consequences, including death.
How Can I Spot A Stroke?
Recognizing a stroke quickly is crucial for getting timely medical help, which can significantly impact recovery. The F.A.S.T. acronym can help you remember the warning signs of a stroke.

- F: Face drooping: Is there drooping or numbness on one side of the face? Ask the person to smile. Does their smile look uneven or off-balance?”
- A: Arm weakness: Is one arm weak or numb? Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- S: Speech difficulty: Is the person’s speech slurred or strange? Ask them to repeat a simple sentence. Can they do it correctly?
- T: Time to call emergency services: Should any of these symptoms occur, contact emergency medical services immediately by calling 911, as timely intervention is critical.
How Can Addiction Treatment Help Lower Stroke Risk?
Treating addiction is an important step in lowering stroke risk, especially since drugs like cocaine, meth, and excessive alcohol can directly damage blood vessels and increase blood pressure.
At Northern Illinois Recovery Center in Crystal Lake, Illinois, we offer the following treatment programs that cater to the needs of people with addiction and mental illness. As a result, these levels of care can help prevent the risk of a stroke and heart attack:
The first step is safely removing the substance from the body. Our drug and alcohol detox center, often with medical help, manages withdrawal symptoms and reduces health risks.
Behavior therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) aim to help individuals understand and change the behaviors and thoughts linked to substance use. This improves long-term self-control and reduces relapse.
Groups like Narcotics Anonymous (NA) or Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) provide community support and accountability, which are important for long-term recovery and stress reduction.
Quitting substance use is just one part; improving diet, exercise, sleep, and stress management can further lower stroke risk.
Many people with addiction also have mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety disorders. Treating these co-occurring mental health disorders helps prevent relapse and supports overall brain and heart health.
Northern Illinois Recovery Center Aims To Educate Those In Recovery
At Northern Illinois Recovery Center in Crystal Lake, IL, we’re committed to educating those in recovery about the risks associated with drug use and its potential consequences, including stroke. We believe that education and awareness are critical to preventing strokes and improving overall health outcomes for individuals in recovery. Our Xanax drug rehabilitation center also provides specialized support for those struggling with Xanax dependence.
Our programs are designed to help individuals understand the importance of maintaining a drug-free lifestyle and provide them with the tools and resources to live a healthy, fulfilling life. Contact us today!






