Both amphetamines and methamphetamines are stimulant drugs. Amphetamines were the first drugs of this type developed, followed by methamphetamines early in the 20th century. Methamphetamine is a synthetic drug which means it’s made completely in a lab. It is one of the most powerful stimulant drugs and has a high addiction potential. Northern Illinois Recovery Center is a drug and alcohol rehab center in Illinois that people can trust for help with amphetamine or methamphetamine treatment.
Jump to Section
Which came first: amphetamine vs. methamphetamine?
According to the University of Arizona’s MethOIDE drug education site, a Romanian chemist first made amphetamines at the University of Berlin in 1887. Six years later, a Japanese chemist made methamphetamine in his lab. Pharmaceutical companies began to market amphetamines for asthma, hay fever, and colds in the 1930s. The British, German, Japanese, and U.S. governments all developed injections or tablets for troops during World War II. The purpose of the drugs? To increase endurance and reduce fear in combat.
Is there a difference between methamphetamine vs. amphetamine?
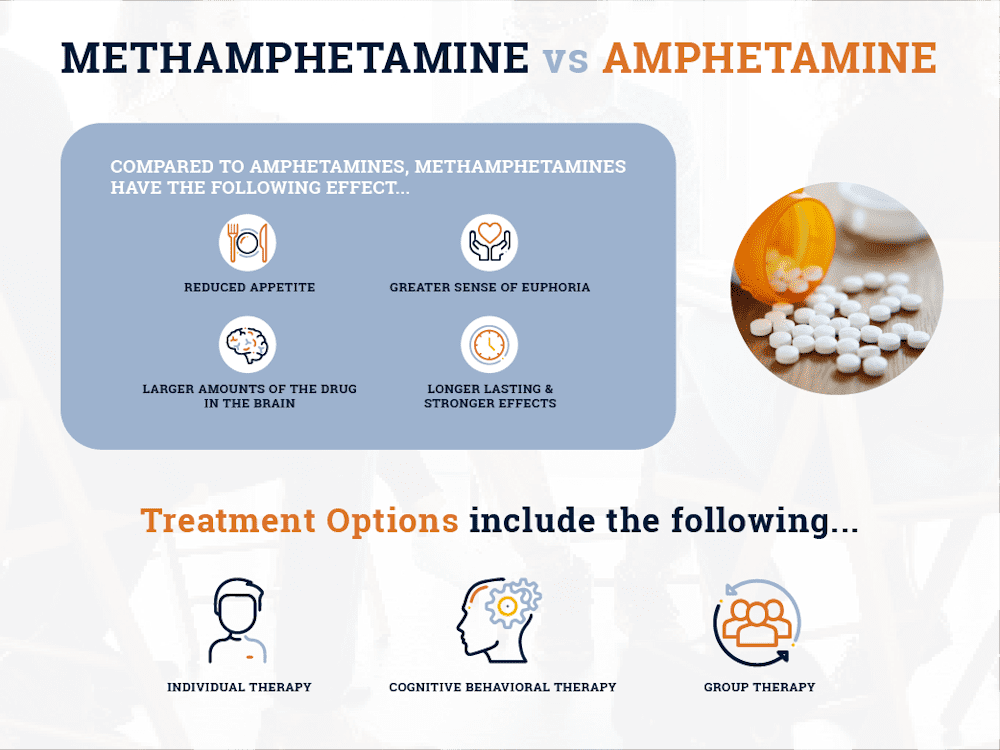
Both drugs are similar in chemical composition, but the small chemical differences between methamphetamine and amphetamine make meth a stronger stimulant drug. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Taken in the same doses, methamphetamine can have the following increased effects compared to amphetamine:
- Reduced appetite
- Greater sense of well-being or euphoria
- Greater amounts of the drug in the brain
- Longer lasting and stronger effects
Which drug has more potential for abuse, methamphetamine vs. amphetamine?
Methamphetamine directly increases the amount of dopamine in your brain. Amphetamine does as well, but at a lower level. Meth lasts longer than amphetamine and it stays in your body longer.
Both meth and amphetamine have potential for abuse. Methamphetamine has a greater potential for tolerance and dependency than amphetamine. Tolerance in methamphetamine users can have long-lasting effects. Some of the results of methamphetamine tolerance include:
- Need to take more methamphetamine to feel the same effect
- Need to take the drug more frequently
- Difficulty feeling any pleasure outside of methamphetamine
What are some effects of methamphetamine vs. amphetamine on the brain?
Methamphetamine has a profound effect on the brains of people who are misusing it. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), meth alters the way your brain functions. In addition to reducing your brain’s natural ability to use dopamine, meth interferes with memory and learning ability. Long-term meth use changes your brain, potentially interfering with your relationships and performance at work, in school, or at home. Amphetamine can have similar effects, but because it is a weaker drug that doesn’t stay as long in your body as methamphetamine, its effects are weaker and shorter-lasting.
Do you need help to stop using methamphetamine?


If you’re struggling to stop using methamphetamine or amphetamine, help is available. The sooner you can reach out for treatment, the more you’ll increase your chances of long-term recovery. Northern Illinois Recovery offers compassionate, individualized rehab programs for people seeking recovery from methamphetamine or amphetamine use along with other drugs and alcohol. Contact us at 855.786.1978 to learn how you can start your recovery today.


Licensed Physician and Surgeon
Dr. Beth Dunlap, a board-certified addiction medicine and family medicine physician, and is the medical director at Northern Illinois Recovery Center. She is responsible for overseeing all the integrated medical services at both campuses. Beth completed medical school, residency, and fellowship at Northwestern University, where she continues to serve on the faculty as a member of the Department of Family and Community Medicine. She has extensive experience in addiction medicine at all levels of care, and her clinical interests include integrated primary care and addiction medicine, harm reduction, and medication-assisted treatment.